Do you want your 3D printed parts to be stronger? By using the right materials and techniques, you can enhance the strength of your parts.
In this post, we give an overview of popular 3D printing materials and their strengths for different uses. Plus, we’ll give you five tips to improve the quality of your 3D printed parts—helping you create long-lasting designs.
How Strong Are 3D Printed Parts?
So, how strong are 3D printed parts? 3D printed parts can be incredibly strong. When created with the right materials, they can withstand pressure up to 9,800 psi and temperatures as high as 428 degrees Fahrenheit. Their strength makes them perfect for testing design concepts and functioning as replacement parts.
What’s the Strongest 3D Printing Material?
It can be hard to choose the right 3D printing material that meets your needs. Which material will make your parts stronger and more durable? Below, we list common 3D printing materials and their strengths across different applications.
How Strong Is PLA?
Polylactic acid (PLA) is one of the most popular 3D printing materials because it’s both strong and cost-effective. It has a tensile strength of 7,250 psi, which allows it to support heavy loads without breaking. PLA is also less expensive than other materials, making it ideal for prototyping and conceptual modeling.
How Strong Is ABS?
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is another commonly used type of 3D printing filament. Although ABS has a moderate tensile strength of 4,700 psi, it’s highly flexible and can withstand heavier impacts than other materials. It can also resist temperatures up to 392degrees Fahrenheit.
Despite its moderate tensile strength, ABS is more durable over time. For this reason, it’s often used to create pre-production parts that must withstand wear.
How Strong Is Nylon?
Similar to ABS, nylon is flexible and can withstand high temperatures up to 428 degrees Fahrenheit. It has a tensile strength of 7,000 psi, placing it just below PLA in terms of strength.
Its durability and strength are perfect for creating end-use parts like door handles and radiator grills, which must retain their form over time.
How Strong Is PETG?
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified (PETG) is often used in industrial applications. The material is dense and rigid with a tensile strength of 7,250 psi. Its strength helps it resist heavy impacts and repeat use.
PETG filament is often used to create parts that require shock-resistance or flexibility, like snap-to-fit components. It’s also chemically neutral and food-safe, making it a popular option for food packaging and containers.
5 Expert Tips to Increase the Strength of 3D Printed Parts
To create 3D printed parts that are built to last, you must use the right materials and techniques. Here are five ways to increase the strength of your 3D printed parts:
1. Choose a 3D Printing Material that Meets Your Needs
The strength of your printed part depends on how closely the material you use matches the application of the part. If you need a part that has a high tensile strength, then you should consider using a material like PLA or PETG. If your part needs to withstand high temperatures, then you should use a heat-resistant material like ABS.
To determine the best material for your part, consider how your part will be used. Will it need to resist high temperatures or carry heavy loads? Select the material that performs best for that purpose.
2. Increase the Infill Density
In addition to choosing the right materials, you should also pay attention to 3D printer settings. One setting that has a significant impact on strength is infill density. This is how much material is packed into the walls of the 3D printed part. Increasing your infill density will result in a stronger 3D printed part that can withstand a heavier impact.
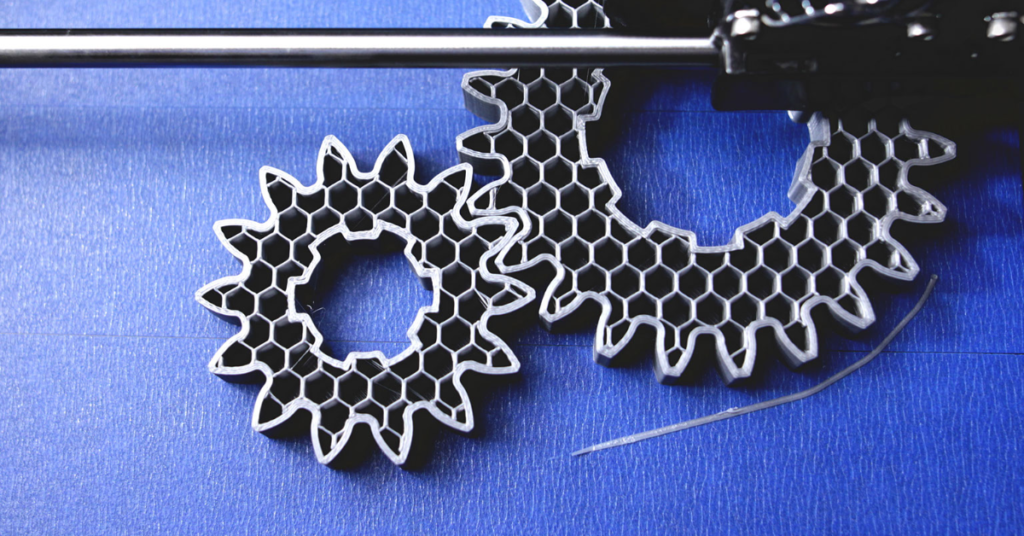
3. Pay Attention to Part Orientation
Part orientation—or the direction your part faces on the 3D printer—also affects its strength. 3D printed parts are strongest when their layers align with the print bed. To strengthen your part, place it on the print bed horizontally so the direction of least stress corresponds with the build direction. This will make your part less likely to shatter under impact.
4. Maximize Your Shell Thickness
Shells are the exterior layers of 3D printed parts. Typically, shells have a thickness of 1.0 to 1.5 mm, but increasing this setting can improve the tensile strength of your part. A thicker shell can also affect impact strength, making your part more resistant to external forces.
5. Use a 3D Printing Company
If your part requires complex materials or designs, consider using a 3D printing company. A 3D printing company will offer a broader range of materials, from nylon to ABS, that may be hard to work with as a beginner. A 3D printing expert can also refine your design to help you produce a stronger part that meets your needs.
Get Started With 3D Printing Today
By choosing the right materials and 3D printer settings, you can ensure your part is built to last. Do you have any questions about how to increase the strength of your 3D printed part? Schedule a free consultation with our 3D printing experts here.



